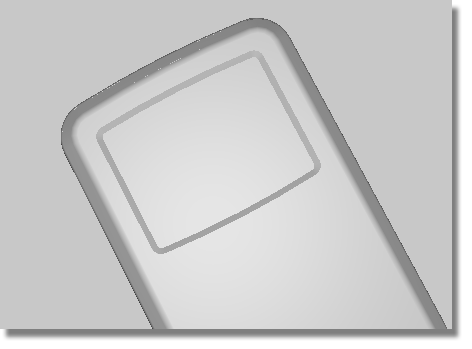
The screen is cut out of the front face of the MP3 player.
You will Offset the outline of the casing to create the screen curves. You will then Project them onto the front face to create Curves-on-Surface. These can then be used to Trim out the aperture for the display screen.
Opening the tutorial file (optional)
If you successfully completed Part 3, proceed to the next step: Creating Offset Curves below.
If you were not successful in part 3, open the file called MP3Player_part4.wire, located in the wire directory of the CourseWare project. This file contains the completed model from Part 3.

Watch Part 4 of the tutorial.
To keep the structured style of the design, the shape of the screen will echo the curve at the top of the MP3 player.
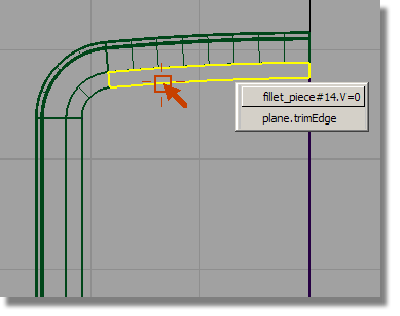
Start by duplicating the edge of the top surface to create a reference curve.
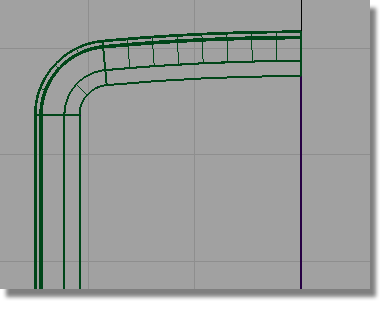
 and select the lower edge
of the fillet surface at the top of the casing.
and select the lower edge
of the fillet surface at the top of the casing.
You will get a choice of picking the edge of the fillet surface or the edge of the plane.
Select the edge of the fillet. This will give you a good quality curve.
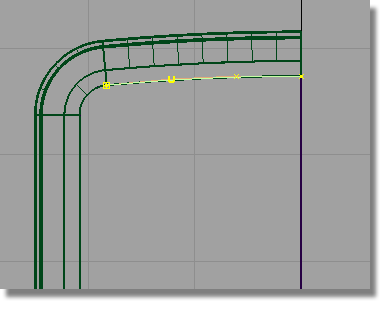
A curve is created that is a duplicate of the surface edge.
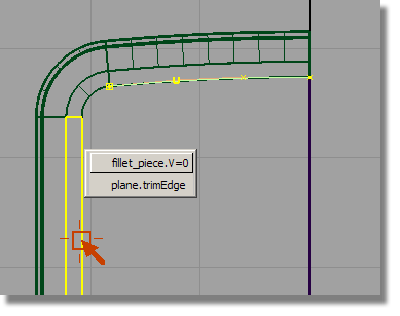
 tool already active, select
the fillet surface at the left side.
tool already active, select
the fillet surface at the left side.
Again, choose the fillet edge, not the edge of the plane.
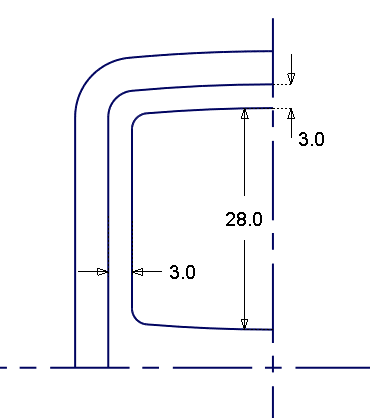
 and type in -3 to
create the top and side curves for the screen.
and type in -3 to
create the top and side curves for the screen.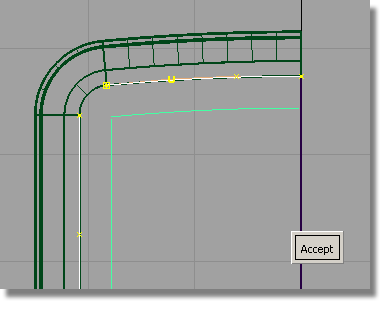
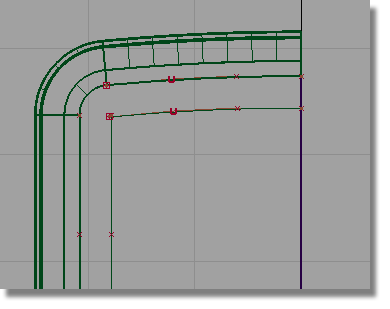
Now you will duplicate and mirror the top curve to create the lower curve.
This time you will use a different technique for mirroring. The Edit > Duplicate > Mirror tool always mirrors across a grid axis. You will use the Edit > Duplicate > Object tool to mirror across an object’s pivot point.
So first, set the pivot for the curve.
 and select the upper curve.
and select the upper curve.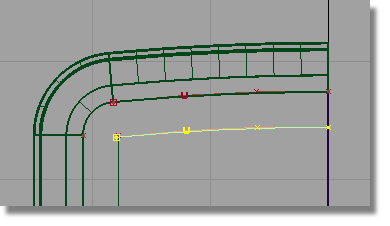
 and use the
and use the  (Windows) or
(Windows) or  (Mac) key to snap the pivot
point to the end of the curve.
(Mac) key to snap the pivot
point to the end of the curve.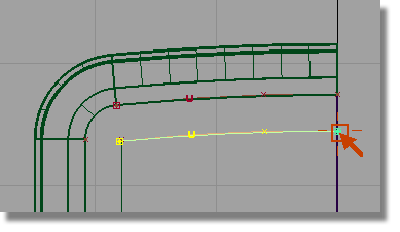
 ❒ to open the option window.
❒ to open the option window.
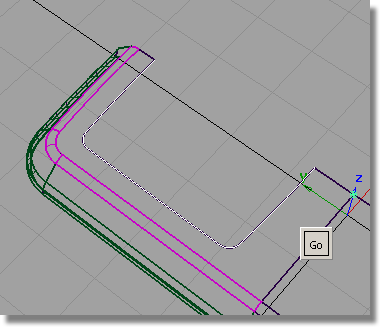
Change the Scaling in the y-direction to -1.
Click Go to create a duplicated curve, scaled in the Y-direction to create a mirrored copy.
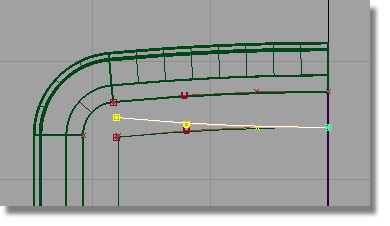
 and type in 0,
-28 to move the curve downward.
and type in 0,
-28 to move the curve downward.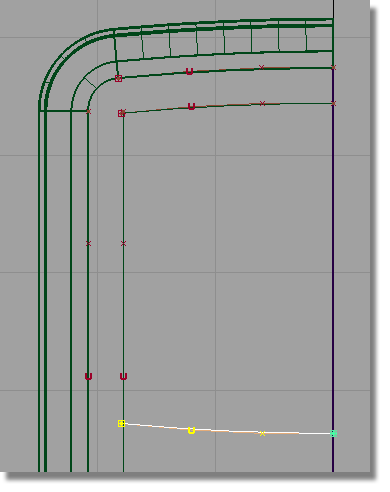
 and follow the prompts to
create fillets between the curves. Set the fillets radii to 2.0
by typing the value on the prompt line.
and follow the prompts to
create fillets between the curves. Set the fillets radii to 2.0
by typing the value on the prompt line.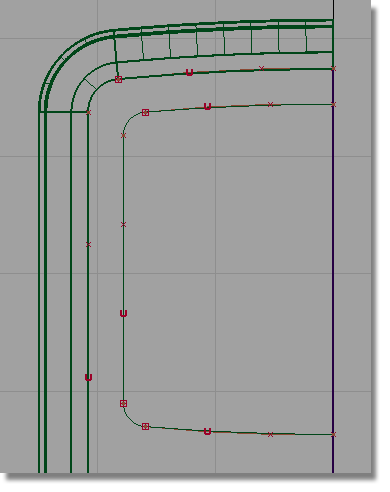
Next, you will Project the curves onto the front surface to cut out the screen shape.
The direction of projection is determined by the active window: the curves will be projected perpendicular to the active window.
By continuing to work in the Top window, you will be setting the direction of projection correctly.
 .
.
You are prompted to select a surface. Pick the plane surface, and click Go.
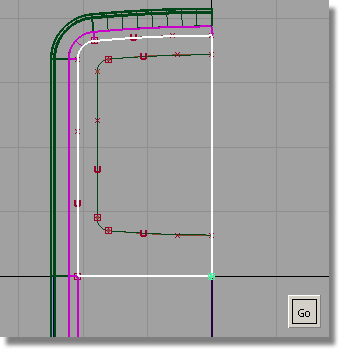
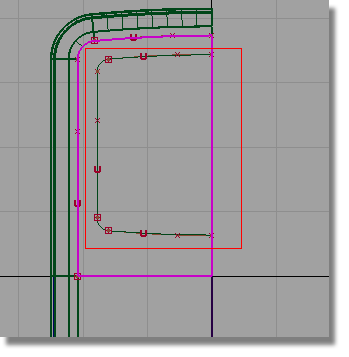
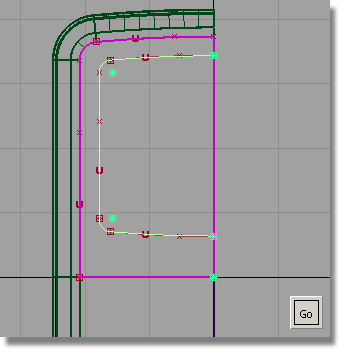
You will now template the curves, so that you can see the curves-on-surface more easily.
 and choose the curves-only option.
and choose the curves-only option.
Drag a pick box over all the curves to select them.
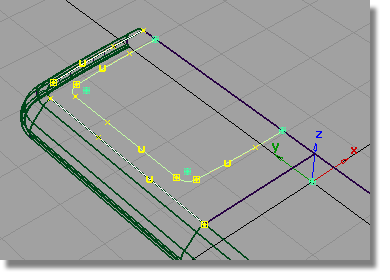
 to template the curves.
to template the curves.
Now you can see the curves-on-surface created by projecting.
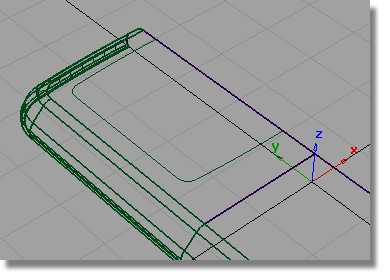
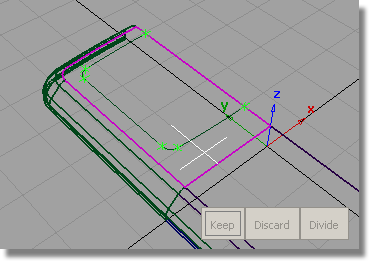
Next, you will trim the front face of the casing to create the opening for the screen.
 . You are prompted to select
a surface to trim.
. You are prompted to select
a surface to trim.
Pick the plane surface.
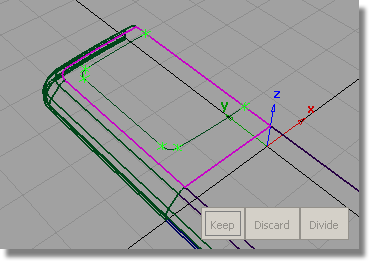
Click the plane surface, outside the screen area.
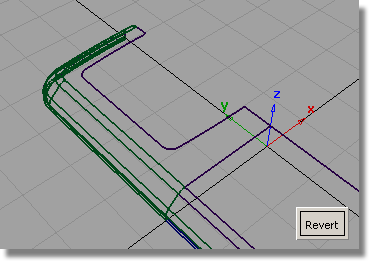
Now you will create a chamfered edge for the screen, and a screen surface.
 . Double-click the icon to
open the option window.
. Double-click the icon to
open the option window.
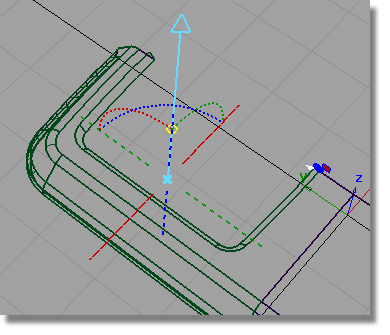
Reset the Construction Type to Draft.
Set the Angle to 45 degrees and the Surface Depth to 1.5.
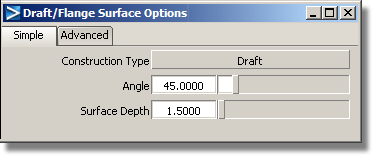
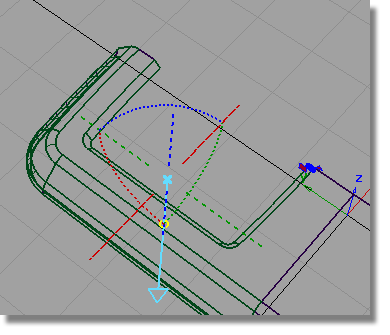
If the surfaces are built in the wrong direction, click the blue dotted line to switch the pull direction of the Draft surface.
To finish off the screen, create a planar surface for the face of the screen.
 and use the curve snap (
and use the curve snap (  and
and  (Windows) or
(Windows) or  and
and  (Mac)) to create a curve
for the center-line of the screen face.
(Mac)) to create a curve
for the center-line of the screen face.
 and select all the lower
edges of the screen chamfer.
and select all the lower
edges of the screen chamfer.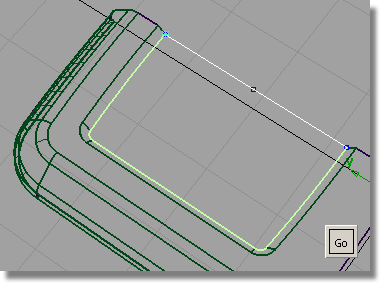
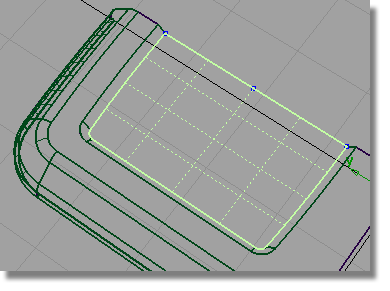
You now have lots of curves, so it’s a good idea to organize them onto a separate layer.
 to create a layer.
to create a layer.
 to select the templated
curves, and Assign them to the new Curves layer.
to select the templated
curves, and Assign them to the new Curves layer.
 to pick any remaining curves
and Assign them to the Curves layer.
to pick any remaining curves
and Assign them to the Curves layer.
(If you want, use the Show menu in the window title bar to turn off the Model and Grid for a better view.)