Limitations related to curve and surface creation and evaluation.


If the edit window is hidden behind the Alias window after
selecting Object Edit > Edit Comment,
bring it to the front using  +
+  or clicking on the TextEdit
application icon in the dock. After entering the text, the TextEdit
application must be closed using Command-Q, or from the TextEdit
application menu at the top of the screen. Just closing the TextEdit
window will not properly close the TextEdit application and save
the text, causing Alias to wait indefinitely.
or clicking on the TextEdit
application icon in the dock. After entering the text, the TextEdit
application must be closed using Command-Q, or from the TextEdit
application menu at the top of the screen. Just closing the TextEdit
window will not properly close the TextEdit application and save
the text, causing Alias to wait indefinitely.

Align does not handle rational geometry as input. Using rational geometry may result in undefined shape

In some situations, curves and surfaces that have been edited using the Symmetry Modeling tool may exhibit abnormal cross sections and associated curvature combs.
Workaround: Zero transform the geometry to fix the problem.
Workaround: When curvature checking using the Evaluate > Check Model  tool (that is Curvature
- G2 is on), consider reducing the Report
Parameters >Curvature Maximum value. The value of
1.0 corresponds to seeing "Flat" as failures. If "Flat" is not a
curvature problem to be identified, set the Curvature
Maximum to a value such as 0.9 or 0.7. Only curvature
deviations greater than Continuity Curvature (from Preferences > Construction Options
tool (that is Curvature
- G2 is on), consider reducing the Report
Parameters >Curvature Maximum value. The value of
1.0 corresponds to seeing "Flat" as failures. If "Flat" is not a
curvature problem to be identified, set the Curvature
Maximum to a value such as 0.9 or 0.7. Only curvature
deviations greater than Continuity Curvature (from Preferences > Construction Options  ) and smaller or equal to Curvature
Maximum are reported as failures and show up in red.
) and smaller or equal to Curvature
Maximum are reported as failures and show up in red.
Workaround: Duplicate all geometry when using symmetric layers.
When you select a canvas and duplicate it, a new infinite plane is created which does not contain all of the canvas plane information (layer stack, name, and so on)
Workaround: Use copy and paste (rather than duplicate) to get the complete canvas information.
If you enable Persistent
sections in the Dynamic Section tool ( Evaluate > Dynamic Section  ), the sections remain visible
even after you exit the tool.
), the sections remain visible
even after you exit the tool.
Workaround: Select all the surfaces that have the persistent sections, go into the Dynamic sections tool again, and then pick nothing.
To resolve this problem turn off the edge-align option.
Construction history that involves symmetry objects means a curve/surface built or modified using a tool that creates construction history and a symmetry object is being used as a constructor (for example, as a gen or path curve in the Rail tool).
Any delete operation (this includes Edit > Cut plus everything in the Delete menu) will also delete all construction history that involves symmetry objects. Undo will bring back the deleted object, but will not restore the construction history.
 (with Preserve
Position off) constructor and target objects that have
been grouped together (for example, a cube and a round on the cube,
an object and an instance of the object), construction history will update.
(with Preserve
Position off) constructor and target objects that have
been grouped together (for example, a cube and a round on the cube,
an object and an instance of the object), construction history will update.
For example, a surface continuity locator created between a surface and its symmetric half is deleted if you save a file.
 tool, is scaled twice.
tool, is scaled twice.
Zero transform the geometry before evaluating the curvature on its cross sections.
 sometimes depends on the
order of picking the input curves.
sometimes depends on the
order of picking the input curves.
Some input curves to Combine curves may result in unsatisfactory results, accompanied by the following warning message:
Curves are too complex. Approximation may be inaccurate.
Picking the curves in a different order often corrects the problem. Try picking the second curve first.
 with the Rebuild
Type set to UNIFORM KNOTS on
a curve-on-surface creates an inexact copy. The
results may not be within the specified tolerance of the original
curve.
with the Rebuild
Type set to UNIFORM KNOTS on
a curve-on-surface creates an inexact copy. The
results may not be within the specified tolerance of the original
curve.
To avoid this problem, use the CHORD parameterization Rebuild Type when duplicating curves on surface.
Unless the U and V directions are at 90 degrees in world space, then you cannot use the manipulator to get the other alignment.
Make sure that the curves are correctly aligned. Dolly in if necessary to see more clearly.
To fix a specific U, V, or Normal alignment, you must select that alignment from the editor window menu.
Workaround: Use the uniform option when the scale of the models to which the blend curve is being attached is very large.

The selection order in Tubular Offset affects the result. When selecting two overlapping surface curves, the primary (selected first) curve is used for building the Tubular offset offset. The secondary surface curve is only used for selecting surfaces to automatically intersect. When box picking is used to grab both surfaces at the same time, you have no control over which curve is first to create the tube with—the results will depend on how the model is loaded in memory. For more consistent results, click on a surface edge and use the pick chooser to select the primary surface edge.

The tube surface now has the Bezier Surfaces check box. If it is checked on, the tube surface will be built with multiple single span surfaces to avoid gaps between surfaces.
Bezier patches have a single span.
 . Set Scope to NEW
SURF, and turn on CVs and Hulls.
. Set Scope to NEW
SURF, and turn on CVs and Hulls.
 tool always trims the surfaces
to try to keep the center of the surface.
tool always trims the surfaces
to try to keep the center of the surface.
Workaround: If the automatic trimming in Ball
Corner is incorrect for a particular model, untrim the
surface and use the Surface Edit > Trim > Trim Surface  tool to explicitely specify
the part you want to keep. Ball corner history is kept and your
trim choice will be maintained, keeping the surface properly trimmed
if the ball corner surface is recalculated.
tool to explicitely specify
the part you want to keep. Ball corner history is kept and your
trim choice will be maintained, keeping the surface properly trimmed
if the ball corner surface is recalculated.
Solution: Reselect the ball corner tool by clicking on its icon. Reselecting the tool will help guarantee it's picking up the current tolerance settings. This is not only applicable for Ball Corner, but for other tools as well when tolerances have changed — not just via file retrieval, but also when editing the Construction Options. Restarting a tool after the tolerances have been changed will help ensure the tool is picking up the new tolerances.
 may not be able to create
a fillet with a surface that has two intersecting points.
may not be able to create
a fillet with a surface that has two intersecting points. 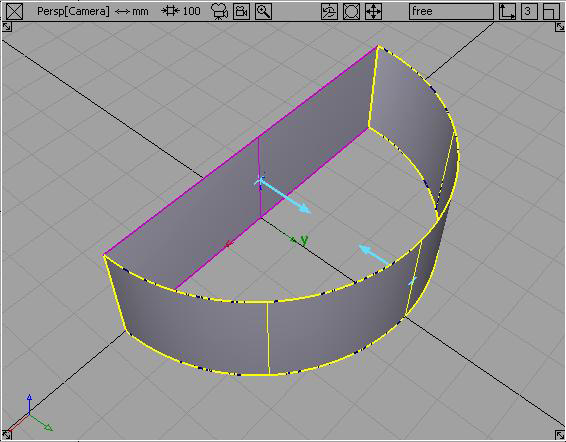
If there are two surfaces intersecting one another at more than one point, detach one of the surfaces so they only have one common intersection.
 Surface Evaluation
> Draft Angle may not display the correct angle.
Surface Evaluation
> Draft Angle may not display the correct angle.
Choose Transform > Zero Transforms  for the surface you are
evaluating to update the draft angle display.
for the surface you are
evaluating to update the draft angle display.
If the surfaces are trimmed, untrim them, create the fillet, then trim them.
Change the position of the pivot points manually and reset the local axes to reflect the proper working environment.
Manually set the Degree and Spans values to produce the desired result.
 tool, Alias may run
out of memory trying to achieve a good fit.
tool, Alias may run
out of memory trying to achieve a good fit.
When dealing with huge numbers of spans on curves-on-surfaces being duplicated, separate the curve-on-surface into manageable chunks before performing the duplicate operation.
 ❒ (TUBE option)
has problems with multiple CVs on the path curve.
❒ (TUBE option)
has problems with multiple CVs on the path curve.
When you are using TUBE mode in Extrude, avoid path curves with multiple CVs on them, as the resulting extruded surface may have undesired twists near the multiple CVs in the path.
 When
creating fillets with the Mesh > Mesh Edge Reconstruct tool,
the type of fillet built is the same as built by the Surfaces > Surface Fillet tool
with Flow Control set to Extend for
both Start and End.
If the fillet surface is not acceptable and you need more control
over the fillet options, toggle Create Fillet off
in Mesh Edge Reconstruct and build
the fillet using the Surface Fillet tool instead.
When
creating fillets with the Mesh > Mesh Edge Reconstruct tool,
the type of fillet built is the same as built by the Surfaces > Surface Fillet tool
with Flow Control set to Extend for
both Start and End.
If the fillet surface is not acceptable and you need more control
over the fillet options, toggle Create Fillet off
in Mesh Edge Reconstruct and build
the fillet using the Surface Fillet tool instead.
 ), try setting Triangle
selection to Include hidden.
), try setting Triangle
selection to Include hidden.
 ) if it was produced from a
tessellation (particularly if Fast tessellation
was used).
) if it was produced from a
tessellation (particularly if Fast tessellation
was used).
Try using the Accurate tessellation method instead if you plan to cut the mesh.